In the ever-evolving world of technology, Blockchain has become a keyword that has received great attention from many people. It is not only the foundation behind the explosion of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but also a technological revolution that promises to change the way we interact with the digital world. But what is Blockchain and why is it so important? Let’s find out about this interesting technology!
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is best known for its important role in cryptocurrency systems to maintain secure and decentralized transaction records. However, the technology is not limited to the cryptocurrency sector. Blockchain can be used as a data “ledger” in any industry to prevent data from being altered or tampered with.

Since the inception of Bitcoin in 2009, the application of Blockchain technology has become very popular and developed strongly with the emergence of many different cryptocurrencies, decentralized finance applications (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs) as well as smart contracts.
Now that we have an overview of Blockchain, let’s dig deeper to find out how this technology works!
How does Blockchain work?
You may be familiar with spreadsheets or databases in your daily work. Blockchain is essentially the same, it is a database where information is entered and stored. However, the main difference between a traditional database or spreadsheet and Blockchain is how the data is structured and accessed.
Blockchain essentially acts as a distributed digital ledger where each transaction is recorded in a transparent and immutable manner. You can simply think of Blockchain as a chain of blocks, where each block contains data about a specific transaction. When a new transaction is made, the information is recorded in a new block, and then this block is cryptographically linked to the previous block, forming a continuous chain.
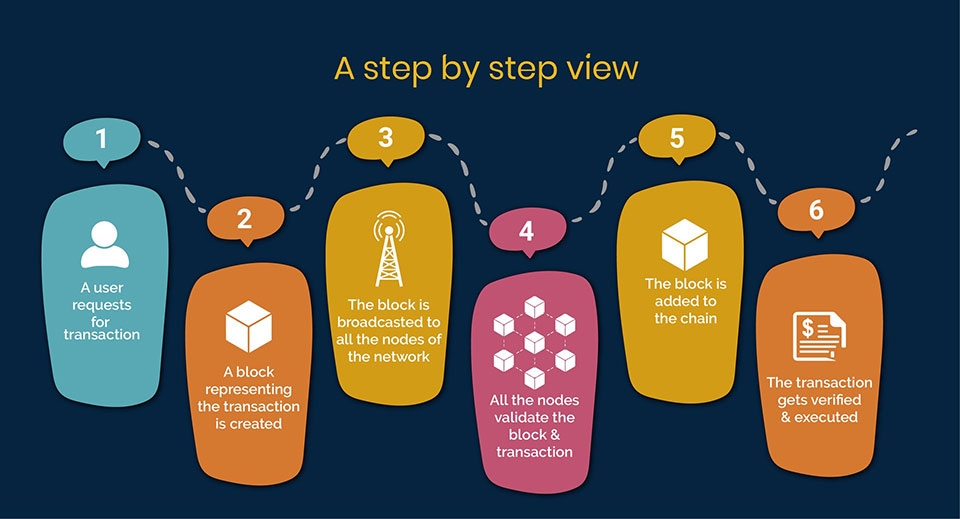
The unique feature of Blockchain is that it is decentralized and not centralized. There is no single organization that manages this ledger. Instead, each node in the Blockchain network will keep a copy of the ledger, ensuring transparency and being difficult to attack or cheat. Every time a new transaction is added, it must be confirmed by a large number of nodes in the network, thereby ensuring the accuracy and security of the information.
What are the types of blockchain?
Blockchains come in three main types:
- Public Blockchain : This is an open blockchain that allows anyone to participate, verify, and make transactions. Typical examples of this type of Blockchain are Bitcoin and Ethereum. In the Public Blockchain type, all transactions are public and transparent, but no one can control or change the data recorded on the Blockchain.
- Private Blockchain : Unlike Public Blockchain, Private Blockchain only allows participation by specific users. This type of Blockchain is often used in organizations or businesses to ensure that access and transaction rights are strictly controlled. Private Blockchain helps increase security and management efficiency compared to Public Blockchain.
- Permissioned Blockchain : This is a form of Private Blockchain, but users are provided with some other privileged features depending on the third party provider. Permissioned Blockchain is often used in corporate environments to ensure high flexibility and control over access and transaction rights.
What versions of Blockchain are there?
Blockchain has evolved through many versions with different applications and features:
- Blockchain 1.0 : This is the first version of Blockchain, which focuses on creating and managing cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. The main goal of this version is to provide a secure and intermediary-free digital payment method.
- Blockchain 2.0 : Developed from Blockchain 1.0, this version extends the application of Blockchain to smart contracts and financial applications. Ethereum is a prominent example of Blockchain 2.0, where users can create and execute smart contracts on a decentralized platform.
- Blockchain 3.0 : This version expands the application of Blockchain beyond finance, including healthcare, elections, resource management, logistics, and many other areas. The goal of Blockchain 3.0 is to leverage the transparency and decentralization of blockchain technology to improve efficiency and safety in work.
Outstanding features of Blockchain
Blockchain stands out with the following features:
- Transparency and immutability : Every transaction on the Blockchain is recorded transparently and cannot be changed once it has been confirmed by the system, thereby enhancing security and reliability.
- Decentralized and decentralized : Blockchain operates without a central governing body. Each node in the network keeps a copy of the ledger, ensuring data integrity and transparency.
- High Security : By using advanced encryption and complex transaction confirmation mechanisms, Blockchain ensures that data cannot be hacked or altered without authorization.
- Automation through smart contracts : Blockchain enables the creation and execution of smart contracts, automating processes and transactions without human intervention.
These characteristics contribute significantly to making Blockchain a revolutionary technology, with the potential for widespread application in many diverse fields, such as finance, healthcare, supply chain management, as well as information security.
Applications of Blockchain
With high security and absolute transparency, Blockchain has been applied in many different fields, including:
- Cryptocurrency This is the most prominent application of Blockchain, with Bitcoin being a prime example. This technology creates a secure, intermediary-free digital payment system for global users.
- Blockchain smart contracts enable the creation and execution of automated, transparent, and immutable contracts. As a result, this technology is being widely used in major financial systems, real estate organizations, and many other fields.
- Blockchain Supply Chain Management helps track and manage supply chains accurately and transparently, from product origin to distribution. Many businesses such as Walmart, Pfizer, AIG, Siemens and Unilever are experimenting with Blockchain in managing their global supply chains.
- Data security and privacy protection Blockchain is also applied in storing and protecting personal data to prevent fraud and improve information security.
- Healthcare Blockchain can be used to store and manage medical records, making information sharing between stakeholders more secure and efficient.

As you can see, Blockchain is not only limited to the financial sector but also extends to many other industries, bringing revolutionary changes in the way information is managed and exchanged.
What are the limitations of Blockchain?
Although Blockchain technology has been recognized as a major breakthrough in many different fields, we also need to admit that it is not perfect and there are still certain disadvantages that are worth keeping in mind.

Costs related to technology
While Bitcoin adoption can help users save on transaction costs, this does not mean that the technology is completely free. For example, the transaction verification system on the Bitcoin network requires a large amount of energy to operate. Experts estimate that the total amount of energy consumed by millions of devices on the Bitcoin network far exceeds the annual electricity consumption of Vietnam.
Poor speed and data performance

Bitcoin is a clear example of the performance limitations of Blockchain technology, especially in processing transactions quickly. Specifically, the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus system that Bitcoin uses requires an average of up to 10 minutes to complete and add a new block to the existing blockchain. At this speed, it has been calculated that the Blockchain network is only capable of processing about three transactions per second (TPS). This clearly shows that Bitcoin is having difficulty scaling and meeting the increasing transaction processing needs in the current digital age.
Conclude
Overall, it is a technology that has shaped the future of cryptocurrencies and revolutionized the way data is managed in many different sectors. However, not all countries consider cryptocurrencies legal. Therefore, you need to fully understand the regulations and legalities before participating in any decentralized financial market.